Livestock Markets Building Resilience in Arid Lands
Background Narrative
The Feed the Future Kenya Livestock Market Systems (LMS) Activity is funded by USAID, the U.S. government’s development aid agency, and implemented by ACDI/VOCA – a global leader with proven expertise in agriculture, economic growth, resilience, finance, equity, and inclusion. The activity’s goal is to improve people’s resilience – their ability to cope with stresses and shocks – while reducing poverty, hunger, and chronic undernutrition in six counties in northern Kenya – Garissa, Isiolo, Marsabit, Samburu, Turkana, and Wajir. LMS prioritizes collaboration with county governments and leverages the private sector to expand and sustain impact.
Project Objectives
- Expand and diversify viable economic opportunities through hard and soft investments.
- Strengthen institutions, systems, and governance to support the development and competitiveness of livestock and other market systems and successfully manage their natural resources, especially rangeland and water access and availability – two key aspects of pastoral livelihoods.
- Improve human capital to help individuals become more resilient and prepared for economic engagement.
- Fostering collaborative action and learning for market systems
Project Activities & Approaches
Strengthening Livestock Markets
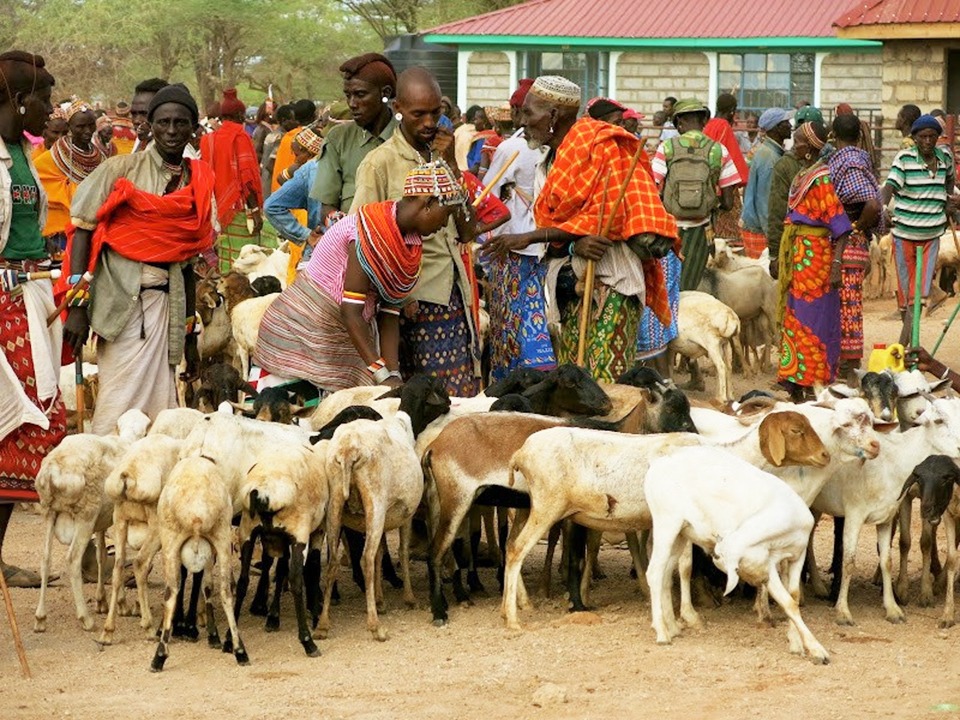
USAID in collaboration with county governments operationalized 36 livestock markets in northern Kenya to boost trade and income for pastoralist families. To improve market management, USAID LMS trained Livestock Marketing Associations (LMAs) on important aspects like leadership, marketing, record keeping, and inclusivity. More importantly, USAID LMS actively advocated for the enactment of market-friendly laws to create a supportive environment for trade. As a result of USAID’s initiatives, 78,617 households recorded a 40 percent increase in household income.
Strengthening Key Business Institutions
USAID LMS played a key role in the growth of key institutions like cooperatives (producer, savings, and credit), Chamber of Commerce and Industry chapters, and ward planning committees, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) by enhancing their access to resources and networks. Through investments in value addition of livestock products – milk and meat. USAID LMS assisted entrepreneurs in the livestock sector to expand their businesses. The Activity also diversified economic opportunities to improve livelihoods and reduce pressure on rangelands. USAID has strengthened 70 cooperatives that were targeted with training and equipment and supported the digitization of 58 cooperatives in the six activity counties.
Support to County Government Legislative Processes
USAID LMS governance and policy work aims to create sustainable, inclusive development in northern Kenya. We work towards equitable allocation of resources that promotes peace and food security. USAID LMS collaborates with other partners to create an enabling environment for communities to access environmental, social, and economic opportunities within the market systems, to reduce poverty and enhance community resilience. We support counties in developing social protection, gender, and youth policies. These aim to reduce gender disparities in access to, control over, and benefit from resources, wealth, opportunities, and services – economic, social, political, and cultural.
From October 2022 to September 2024, USAID LMS assisted communities in northern Kenya to cope with the devastating effects of an unprecedented drought, coronavirus pandemic, food shortages resulting from the war in Ukraine, and severe floods. The interventions contributed to saving communities’ development gains and protecting their livelihoods.
Access to Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene
USAID LMS worked closely with county governments and ward planning committees to rehabilitate 65 community water projects providing sustainable access to clean drinking water to 119,184 people and their livestock out of a target of 120,020 people. The interventions included the repair of damaged borehole components, installing new pipelines and solar-power systems, and refurbishing or constructing water kiosks. To sustain water management, USAID LMS trained water users’ associations (WUAs) on critical topics such as water resource management, community engagement, environmental conservation, gender and social inclusion, and financial management.
Boosting Food Availability for Vulnerable Households
USAID LMS provided economic stimulus support to 5,497 food and livestock traders, benefiting over 428,638 families by improving food and market access. This initiative helped keep businesses afloat and operationalized 36 livestock markets, ensuring the continued sale of livestock, supply of livestock feed to milking animals, and linking households to agrovets, creating over 5,000 jobs. Additionally, 6,712 households, out of a target of 10,350, received nutrient-dense livestock feeds, saving 152,860 livestock valued at $4.7 million from drought-related deaths.
Building Community Capacities
USAID LMS strengthened the roles and interactions of various actors within local systems, such as ward planning committees (WPCs), water users’ associations, livestock market associations, and Girls Improving Resilience through Livelihoods (GIRL). Through the localization approach, the activity marginalized and underrepresented groups by developing their capacities and providing them with the necessary skills and opportunities to lead their growth. USAID LMS also increased funding flows by providing in-kind grants to county governments, SMEs, and chambers of commerce. The goal is to ensure that the solutions implemented are owned by the local community and sustainable even after the activity’s completion.
Project Results
- 78,617 livestock market actors in northern Kenya with 40% increased income. 24,057 women participating in various activities within 36 livestock markets funded by USAID.
- 5,497 traders, (69% women) recorded a 43 percent increase in incomes as a result of USAID start-up grants. The businesses created 1,200 direct and indirect jobs, improving food and market access for 428,638 families.
- 5,000 women and 17,000 adolescent girls in small businesses through training, mentorship, savings groups, and cash transfers, to help break the cycle of poverty.
- 119,184 people out of a target of 120,020 with access to safe and clean water through the rehabilitation of 65 water projects.
- 70 cooperatives established with a membership of over 6,000 people – marketing platforms, providing access to market information, and financial services.
- $916,278 in public and private sector investments facilitated leading to improved food security and nutrition with $531,211 accessed by SMEs and SACCOs for agricultural-related financing
- 34 ward planning committees were established with $8.6 million worth of community priorities implemented through the County Integrated Development Plans.
Resources
View the project’s brochure here.
Gender Brief I – Inclusive Design and Implementation of Grant Portfolio
Gender Brief II – Increased Economic Engagement of Women
Sustainability of Outcomes Brief
Sustainability Assessment Final Report
Outcome Harvesting Final Report